Why Care Is Crucial? Causes, Treatments, and In-depth Prevention
"A deep dive into all aspects of gum health: Why is gum care more important than you think? This article explores the causes of gum disease, warning signs to look out for, and detailed treatment approaches from early to severe stages. We also provide proper prevention methods to build a strong and lasting smile."
ในโลกของการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก หลายคนมักจะให้ความสำคัญกับฟันเป็นอันดับแรก ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเรื่องความขาวสะอาด ความสวยงาม หรือการจัดเรียง แต่สิ่งหนึ่งที่มักถูกมองข้ามไปอย่างน่าเสียดาย คือ “เหงือก” ซึ่งเปรียบเสมือนรากฐานที่คอยยึดฟันให้อยู่ได้อย่างมั่นคง หากปราศจากรากฐานที่แข็งแรงแล้ว ฟันที่ดูสวยงามภายนอกก็ไม่สามารถอยู่ได้อย่างยั่งยืน โรคเหงือกจึงนับเป็นภัยเงียบที่ร้ายกาจ เพราะมันสามารถทำลายเนื้อเยื่อและกระดูกที่รองรับฟันได้อย่างเงียบๆ ในระยะเริ่มต้นโดยไม่แสดงอาการเจ็บปวด จนเมื่อรู้ตัวอีกทีก็อาจสายเกินไป บทความนี้ถูกสร้างขึ้นเพื่อเป็นคู่มือที่ครอบคลุมทุกแง่มุมของสุขภาพเหงือก เพื่อให้คุณเข้าใจและหันมาให้ความสำคัญกับ “รากฐาน” ของรอยยิ้มอย่างแท้จริง
Why Gum Care Is More Important Than You Think
Having healthy gums has a far-reaching impact beyond just aesthetics; it is inseparably linked to our overall health.
1. Prevents Loose and Lost Teeth: Irreversible Damage
The primary function of the gums is to act as a protective barrier and anchor teeth securely to the jawbone. When bacterial plaque and tartar accumulate below the gum line for an extended period, it causes chronic inflammation. This triggers the body's immune system to attack and destroy the gum tissue and supporting bone. The results are "gum recession" and "bone loss." As the supporting bone diminishes, teeth lose their firm anchor and begin to become loose, ultimately leading to permanent tooth loss. This is a type of damage that is difficult to treat and very costly.
2. Prevents Impacts on Overall Health: Gums Are an Indicator of Your Body's Health
2. Prevents Impacts on Overall Health: Gums Are an Indicator of Your Body's Health
- Cardiovascular Disease: The bacteria that live in the mouths of gum disease patients can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body. When these bacteria reach the heart, they can cause inflammation in the coronary arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Diabetes: Gum disease and diabetes have a bidirectional relationship. Diabetic patients are at a higher risk of developing gum disease because their body's ability to fight off infections is reduced. In turn, uncontrolled gum disease negatively impacts a diabetic patient's ability to control their blood sugar levels.
- Respiratory Illnesses: Inhaling bacteria from the mouth into the lungs can increase the risk of pneumonia.
- Pregnancy Complications: Pregnant women with severe gum disease may have a higher risk of giving birth prematurely or having a baby with low birth weight.
3. Reduces Infection Risk: Build a Shield for Your Body
Inflamed gums are an open door for oral bacteria to enter the bloodstream easily. This condition is called "bacteremia," and if left untreated, it can lead to infections in various vital organs. Therefore, keeping your gums healthy is like building a crucial first line of defense for your body.
4. For Confidence in Your Smile: Complete Physical and Mental Health
Beyond the physical effects, gum health directly impacts mental well-being and appearance. Problems such as swollen, red gums, easy bleeding, or chronic bad breath can completely destroy a person's confidence in smiling and speaking with others. Conversely, when gums are healthy, we can smile fully, which positively impacts our personality and social relationships.
The Main Causes of Gum Disease
The cause of gum disease always begins with the accumulation of "plaque," which, if left untreated, turns into "calculus."
- Plaque: This is a sticky, invisible film made of bacteria that grow rapidly in the mouth. If not removed by regular brushing and flossing within 24 hours, these plaques start to produce toxins that trigger gum inflammation.
- Calculus (or Tartar): This is mineralized plaque that has hardened. It typically takes about 1-2 weeks to form. Calculus cannot be removed by normal brushing and requires special tools from a dentist. The accumulated calculus acts as a habitat for bacteria, making it even more difficult to clean the mouth.
Other Risk Factors to Be Aware Of:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Incorrect brushing techniques, not flossing regularly, and not cleaning the tongue thoroughly.
- Smoking: Smoking not only makes gums weak and prone to infection but also constricts blood vessels in the gums, reducing blood flow. This makes the gums less red and swollen than usual, which is why many smokers don't realize they have gum disease.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more susceptible to gum disease than others, even with good oral hygiene.
- Hormonal Changes: Such as during pregnancy, puberty, or menopause, hormonal changes can make the gums more susceptible to inflammation.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Especially diabetes with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, as high sugar levels allow bacteria to thrive and reduce the body's ability to fight infection.
- Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the body's immune system, making it harder to fight off oral infections.
- Diet: Frequent consumption of sugary foods and refined carbohydrates provides fuel for bacteria in the mouth.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as antidepressants, antihistamines, or heart medications, can cause dry mouth, which is a significant factor that increases the risk of gum disease because saliva naturally helps wash away bacteria.
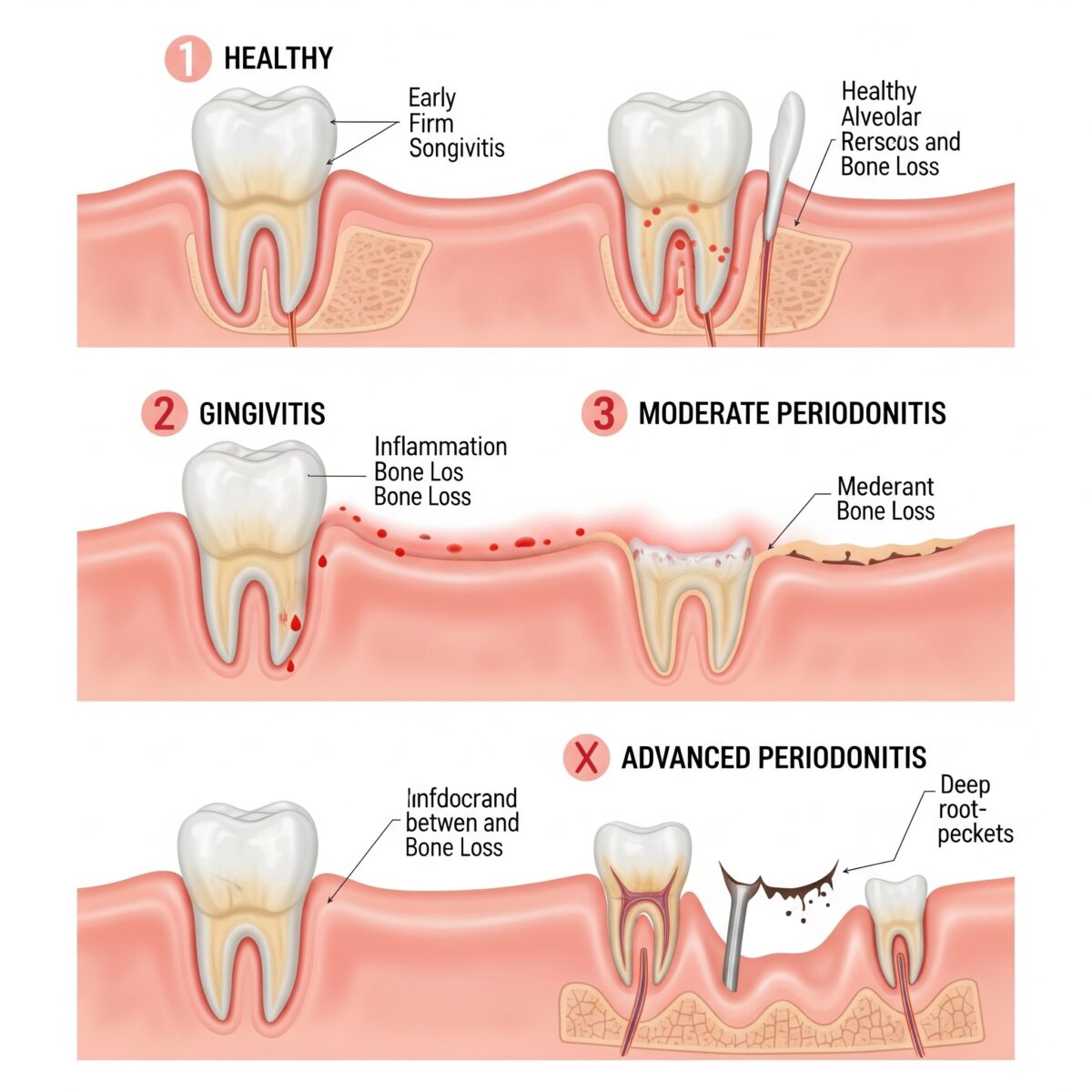
Symptoms of Gum Disease to Observe in Detail
Gum disease is divided into two main stages, with symptoms varying by severity.
1. Gingivitis: The Early Stage That Is Still Curable
- Swollen, Red Gums That Bleed Easily: This is the most obvious symptom. Bleeding occurs even with gentle brushing or flossing.
- Tender Gums: Gums will appear swollen and softer than usual, and may be sensitive to touch.
- Bad Breath: Caused by bacteria accumulating in the gum pockets and between teeth.
If treated correctly at this stage, the symptoms can be fully reversed, and the gums will return to their healthy state.
2. Periodontitis: The Severe Stage with Permanent Damage
When gingivitis progresses without treatment, it becomes periodontitis, which permanently destroys the bone and tissue that support the teeth. This disease can be divided into 3 levels:
- Early Periodontitis: Gums begin to recede, and there is minor destruction of the supporting bone.
- Moderate Periodontitis: There is more significant bone destruction, causing teeth to become slightly loose, and gaps begin to appear between teeth.
- Advanced Periodontitis: There is severe bone destruction, teeth are very loose, affecting chewing, and eventually fall out.
Other Symptoms That May Appear in Periodontitis:
- Gum Recession: Causes tooth roots to be exposed, making teeth look longer.
- Loose Teeth: A result of the supporting bone being destroyed.
- Pus from the Gums: A sign of a severe infection.
- Misaligned Bite: The teeth no longer fit together as they used to.
If you have these symptoms, you should see a dentist immediately for diagnosis and proper treatment planning.
Detailed Treatment and Prevention of Gum Disease
Dental Treatment for Gum Disease:
- Scaling This is the most crucial basic treatment for gingivitis. The dentist will use special tools to remove the hardened calculus and plaque from the tooth surfaces and below the gum line.
- Root Planing: A deeper treatment than scaling, where the dentist meticulously cleans the root surfaces below the gums to remove bacteria and toxins, and to smooth the root surface to prevent future plaque accumulation. This treatment is often done under local anesthesia.
- Gum and Periodontal Surgery: In severe cases of periodontitis, surgery may be necessary to access and clean deep-seated infections. There are several types:
- Pocket Reduction Surgery: The dentist lifts the gums to clean out calculus and bacteria, then sutures the gums tightly back against the teeth.
- Gum Graft Surgery: Used to treat gum recession by transplanting tissue from another area in the mouth to cover the exposed tooth roots.
- Bone Graft Surgery: Used to treat bone loss by adding artificial bone or bone from another source to strengthen the foundation of the teeth.
The Best Prevention is Daily Self-Care:
- Brush at Least Twice a Day: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush correctly at a 45-degree angle to the gums, using gentle sweeping or small circular motions for at least 2 minutes each time. You should change your toothbrush every 3-4 months.
- Floss Regularly: Brushing alone cannot remove all food particles and plaque from between teeth. You should floss at least once a day, preferably before bed, to clean between teeth and below the gum line.
- Use an Interdental Brush: For those with gaps between their teeth, an interdental brush is more effective for cleaning.
- Use Mouthwash: Mouthwash containing antibacterial agents can help reduce the amount of bacteria in the mouth. However, mouthwash cannot replace brushing and flossing.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Getting a dental check-up and scaling every 6 months is extremely important, as the dentist can detect problems early and treat them promptly.
- Change Your Habits: Reducing smoking and controlling the amount of sugar in your diet will effectively reduce the risk of gum disease.
Q&A: Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Disease
- Question: Can gum disease be completely cured?
- Answer: หากเป็น If it's gingivitis,the early stage, it can be completely cured with scaling and good oral hygiene. However, if it's periodontitis, which involves bone loss, the bone cannot be restored to its original state, but the condition can be controlled and prevented from progressing further.
- Question: Is gum disease treatment painful?
- Answer: Regular scaling may cause a slight sensitivity. If there is a large amount of tartar or root planing is required, the dentist will use a local anesthetic so the patient does not feel any pain during the treatment.
- Question: How long does gum disease treatment take?
- Answer: It depends on the severity of the disease. For gingivitis, a single scaling session may be enough. For periodontitis, multiple appointments may be needed for detailed treatment, and regular follow-up appointments may be required.
- Question: How do I know if my oral hygiene is good enough?
- Answer: The best signs are if your gums are pale pink, not swollen, not red, and do not bleed when you brush. Additionally, if you don't have bad breath or a sticky film on your teeth in the morning, your hygiene is at a good level.
Healthy Gums Lead to Healthy Teeth and Overall Health
Investing in gum health is the smartest investment you can make to maintain your oral health and overall well-being in the long run. Don't let a small problem like swollen, red gums become the cause of complex and severe issues in the future.
For organizations that genuinely want to promote employee health, the AT U DENTAL BUS is ready to be your partner. We can bring comprehensive dental services directly to your workplace, so employees can access gum and dental care conveniently without having to take time off work. Because prevention is the most valuable investment.
Interested in a consultation or planning a service for your organization?
- Phone Number: 02-096-4435
- LINE OA: @atudental
- 🌐 Website: www.atudental.co.th
